The Pleistocene transition to meat eating and the evolution of “recreational” drug use
Washington State University
October 1, 2025
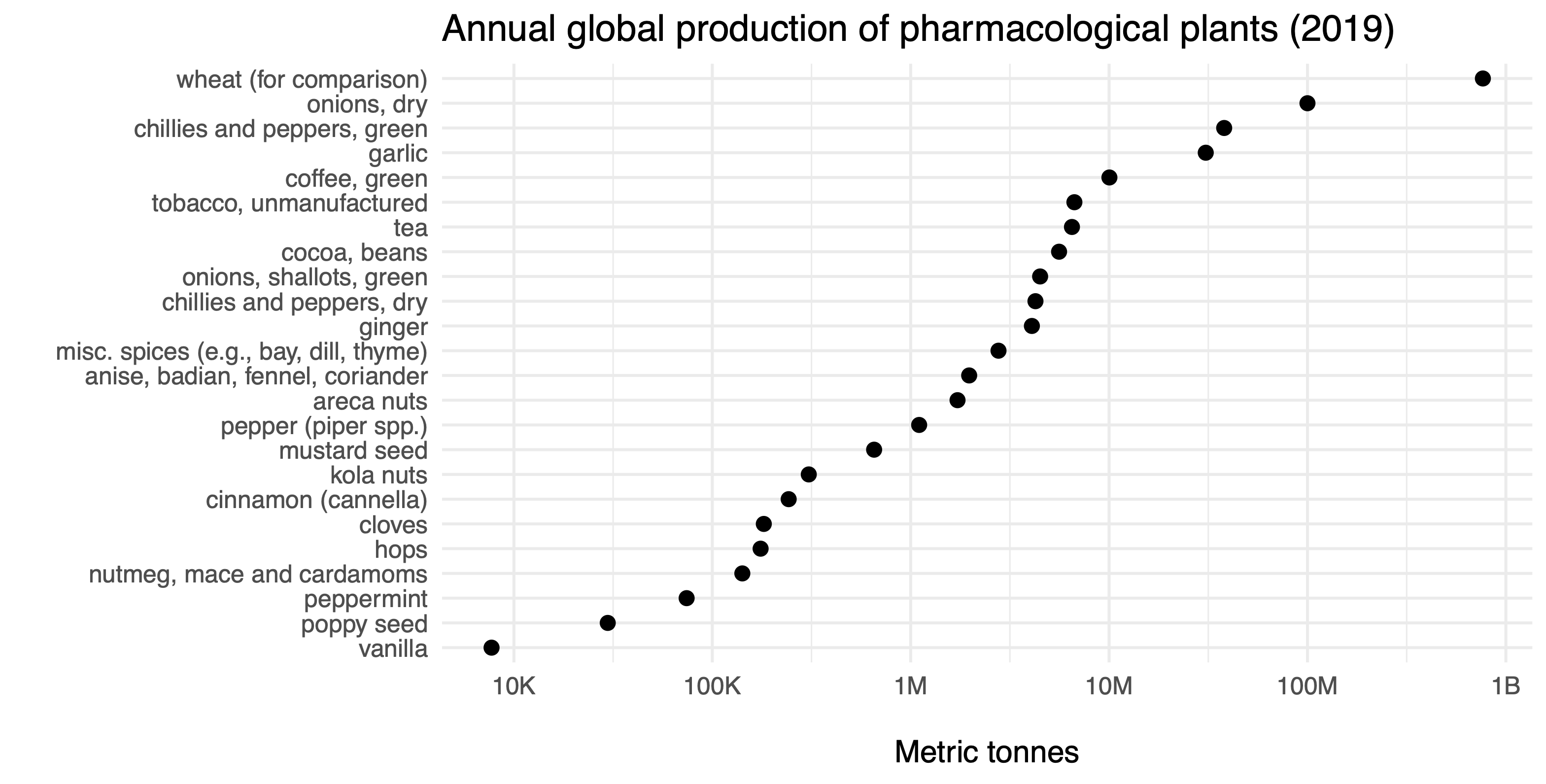
High demand for pharmacological plants has shaped the modern world

Global spice trade 2000 BP (Wang et al. 2023)
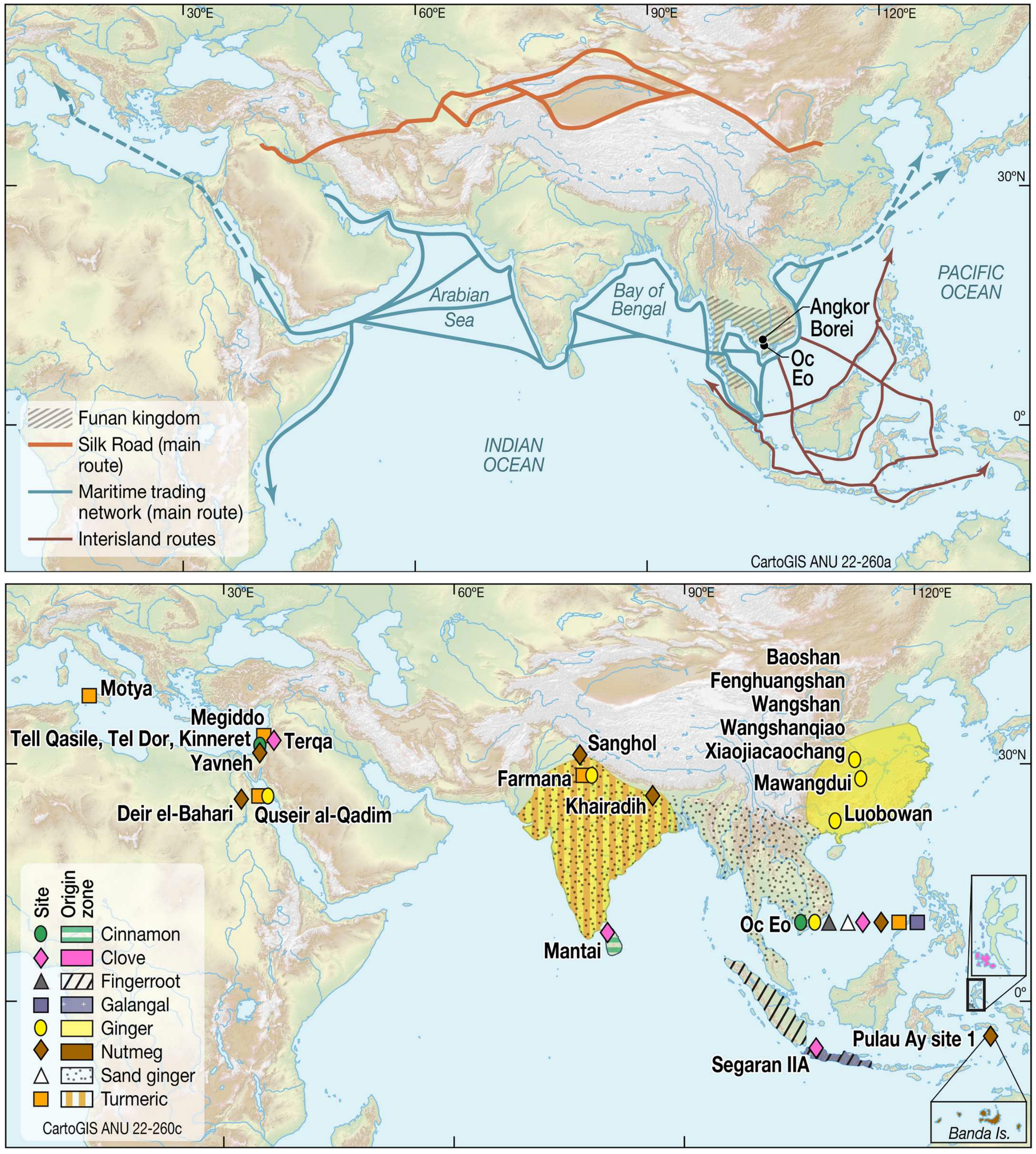
Spice trade 16th century Portugal (De Romanis 2015)
Global spice trade today (Food and Agriculture Organization 2019)
Cocaine export routes

World Drug Report 2025
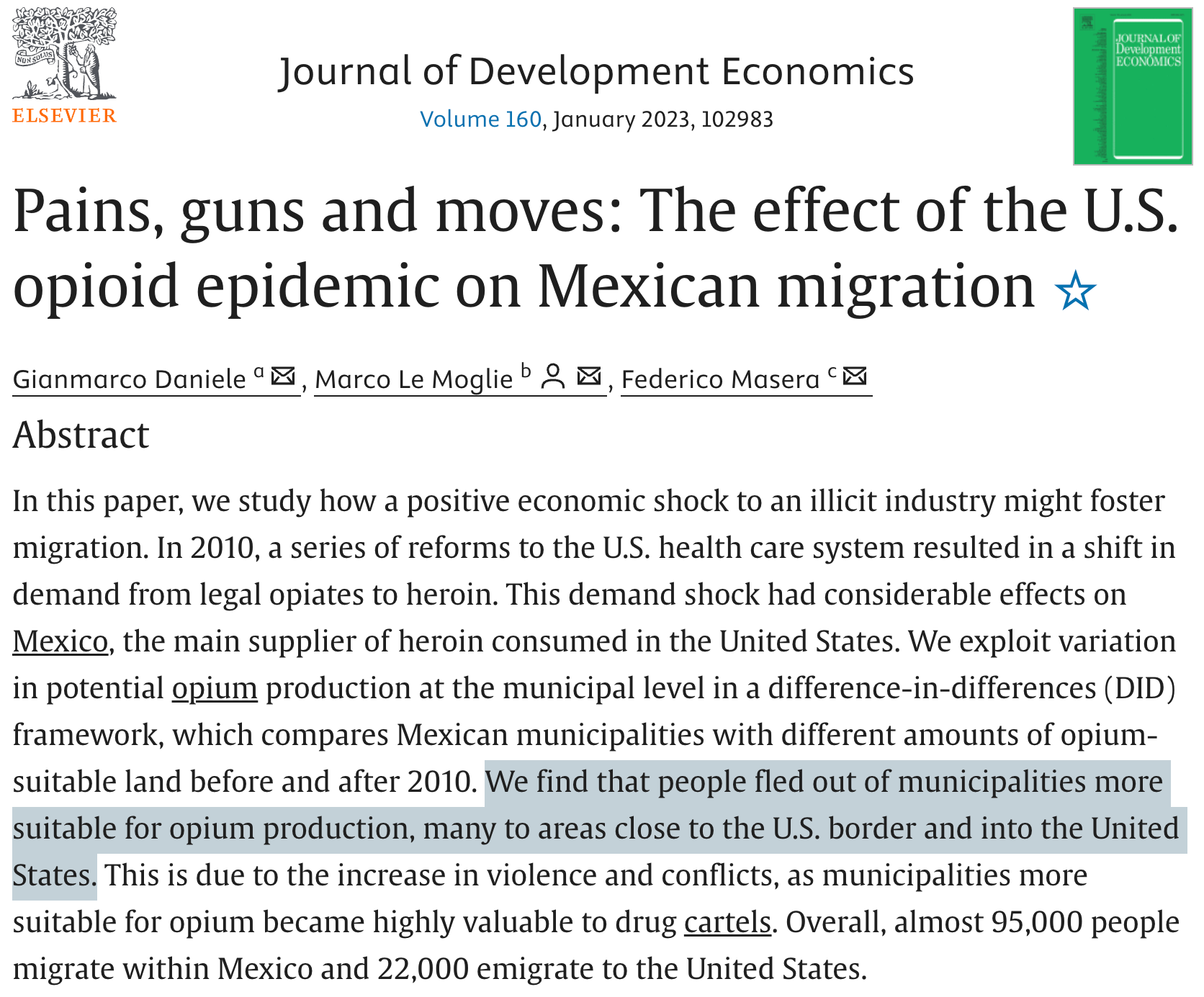
Drug violence and migration (Daniele, Le Moglie, and Masera 2023)
Global drug mortality (Goodchild, Nargis, and d’Espaignet 2018)

Hypothesis
Intensifying zoonotic pathogen pressure in Pleistocene Homo selected for increased pharmacological plant use
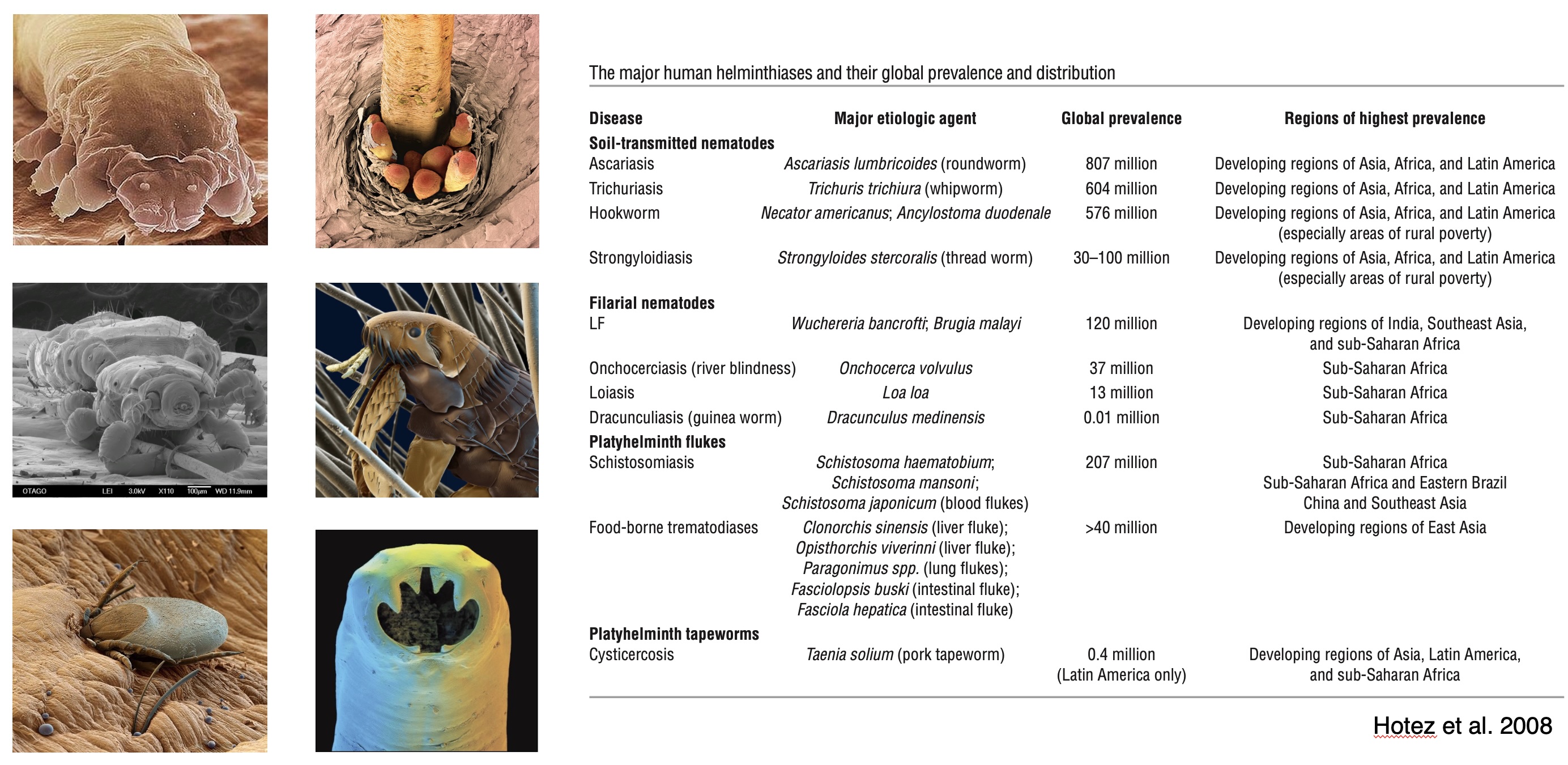
Evolution of the human diet
Hominin Plio-Pleistocene ecology
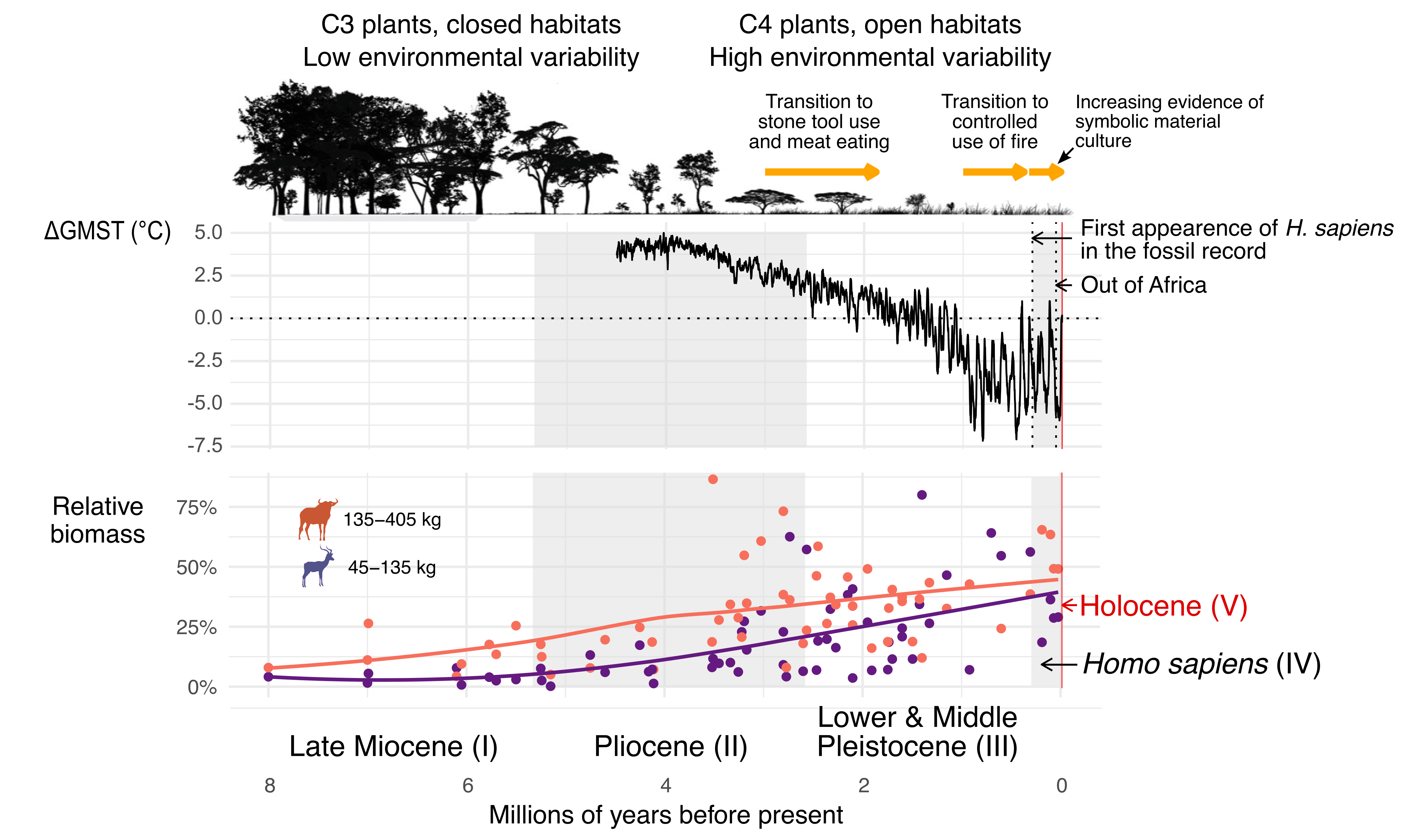
Miocene diet

Hominin Plio-Pleistocene ecology

Pliocene diet
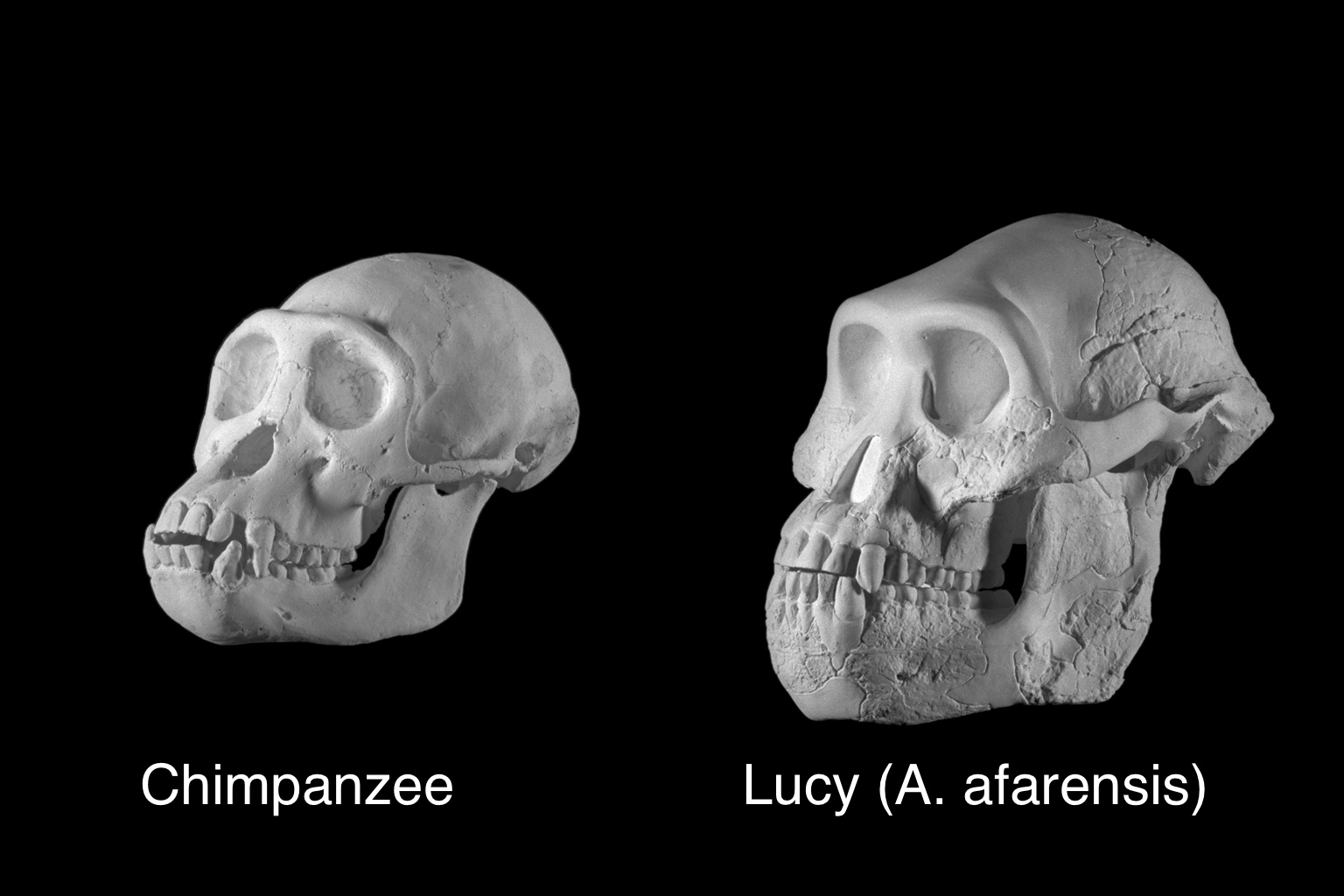
Pliocene diet
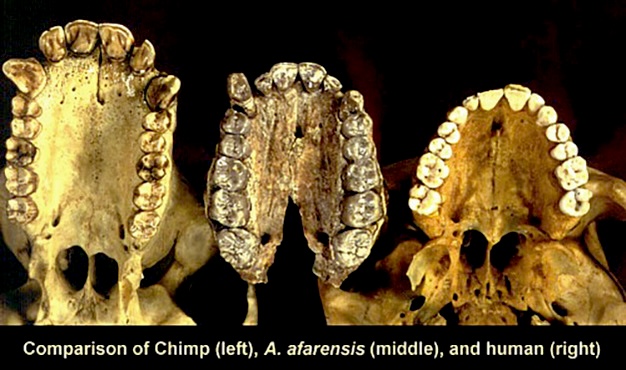
Pliocene diet
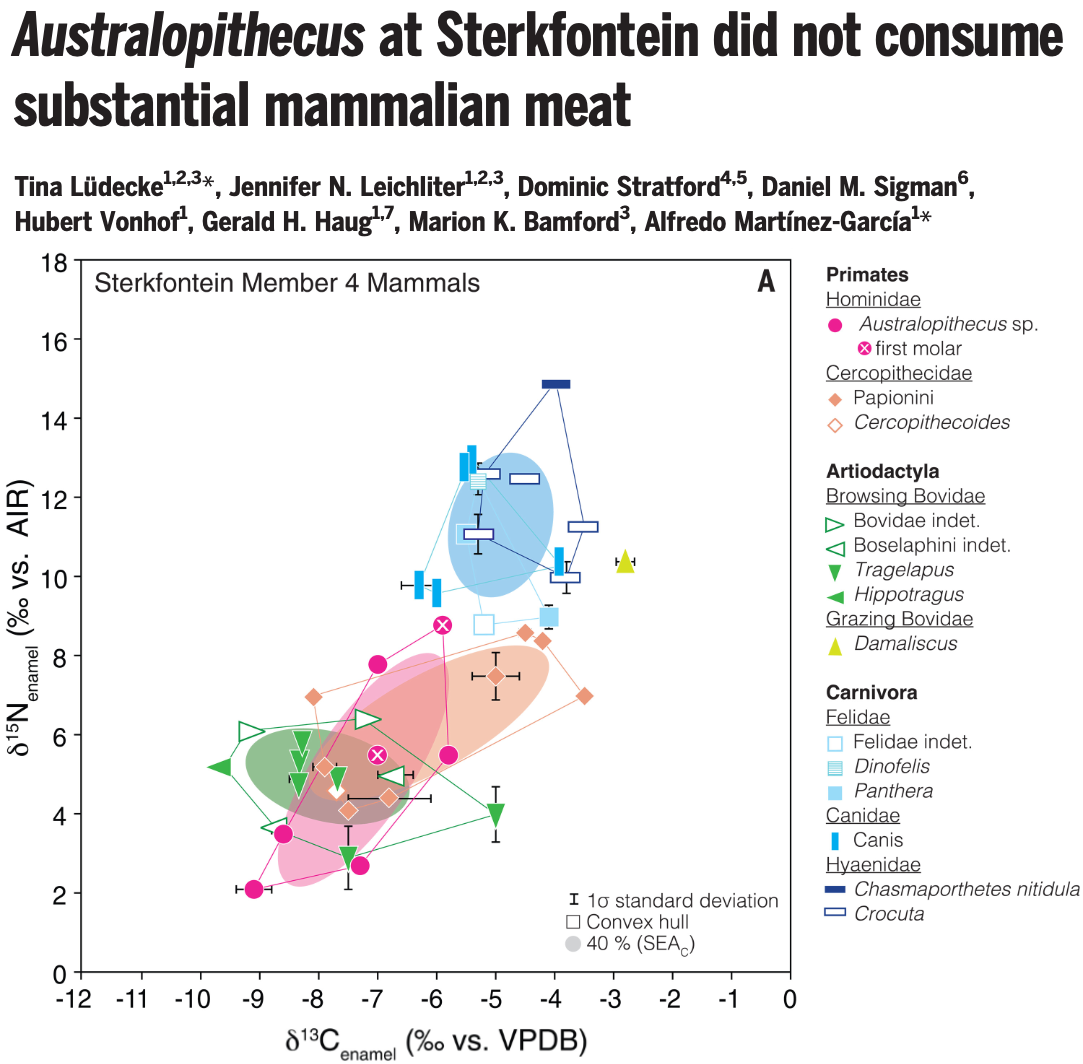
Hominin Plio-Pleistocene ecology

The transition to carnivory
The transition to carnivory

Domı́nguez-Rodrigo et al. (2021)
Dramatic dietary shift
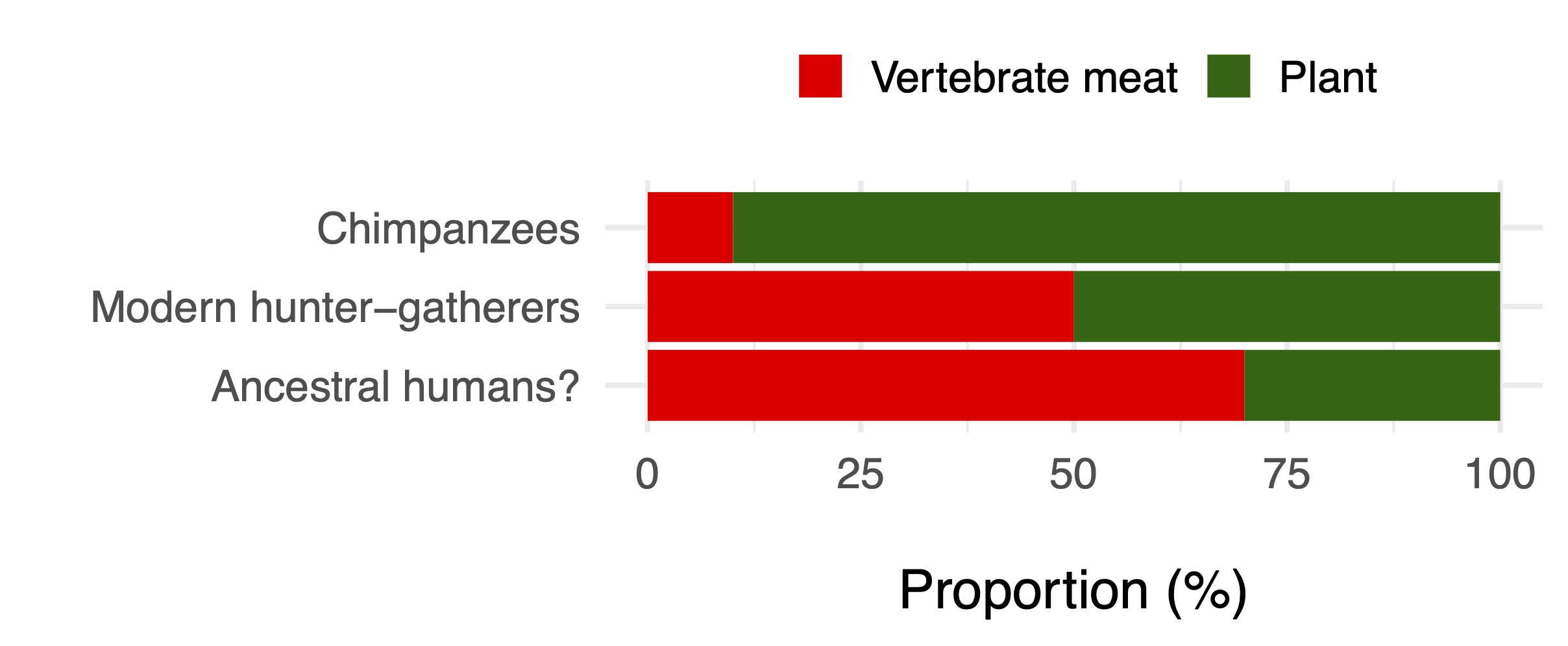
Increased zoonotic pathogen pressure
Plant vs. animal pathogens
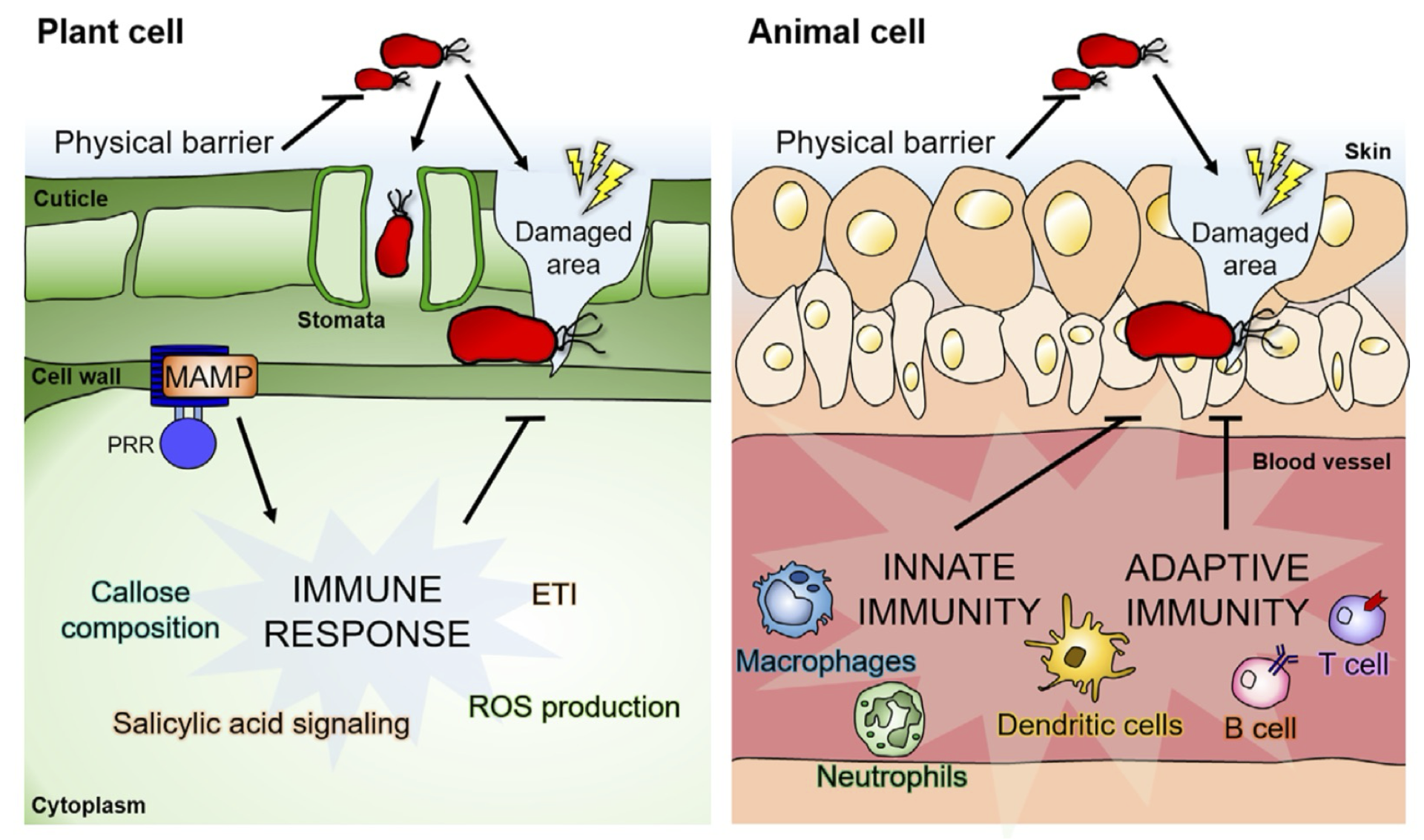
Kim et al. (2020)
Most animal RNA viruses enter human cells
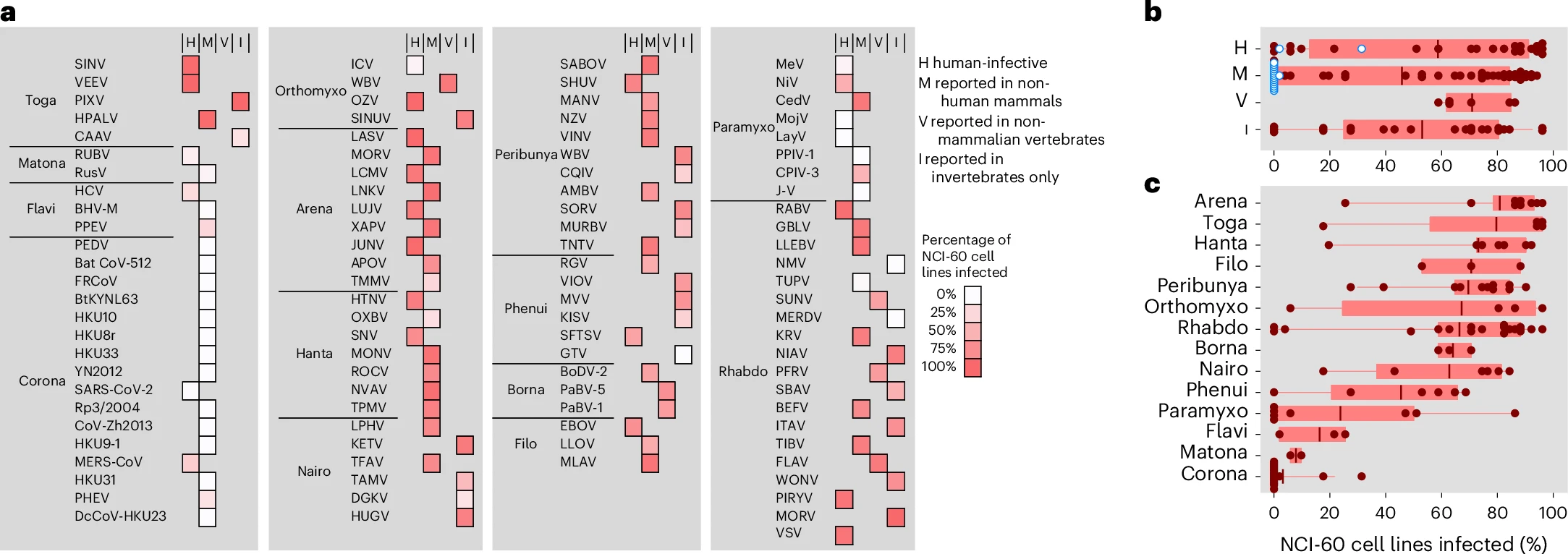
Dufloo et al. (2025)
Wild mammalian zoonotic reservoirs (Han, Kramer, and Drake 2016a)

Han, Kramer, and Drake (2016b)
Bushmeat spillover risk
Ebola, HIV, and monkeypox, SARS-CoV-1, and possibly SARS-CoV-2 (Kurpiers et al., 2016; Peros et al., 2021).
Systematic review: 133 reports of disease involving 60 pathogens in 58 bushmeat species, mostly mammals (95%), with some reptiles (4%) and birds (1%).
The most common zoonotic pathogens were helminths (37%) and bacteria (33%), followed by viruses and protozoa (15% each) (Peros et al., 2021).
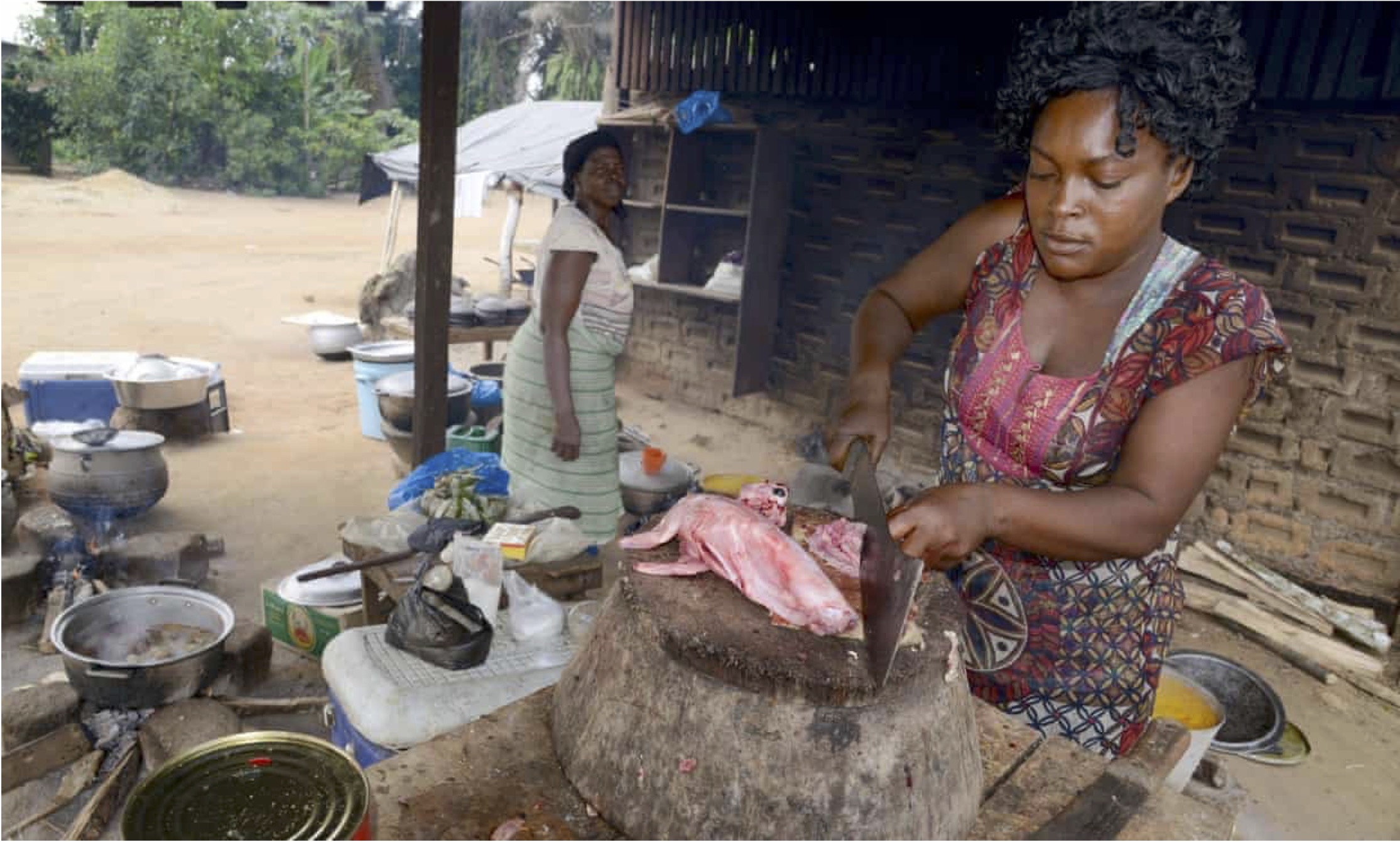

Hunting spillover risk
- Congo Basin foragers (pygmies) are at higher risk of zoonotic spillover than neighboring farmers
- Simian foamy virus (SFV)
- Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)
- Monkeypox
- Ebola (highest prevalence of antibodies ever reported: 18.7% vs. 2-3.5%)
- Severe bites from a non-human primate are major risk factor for infection

RNA virus tissue tropism and transmission
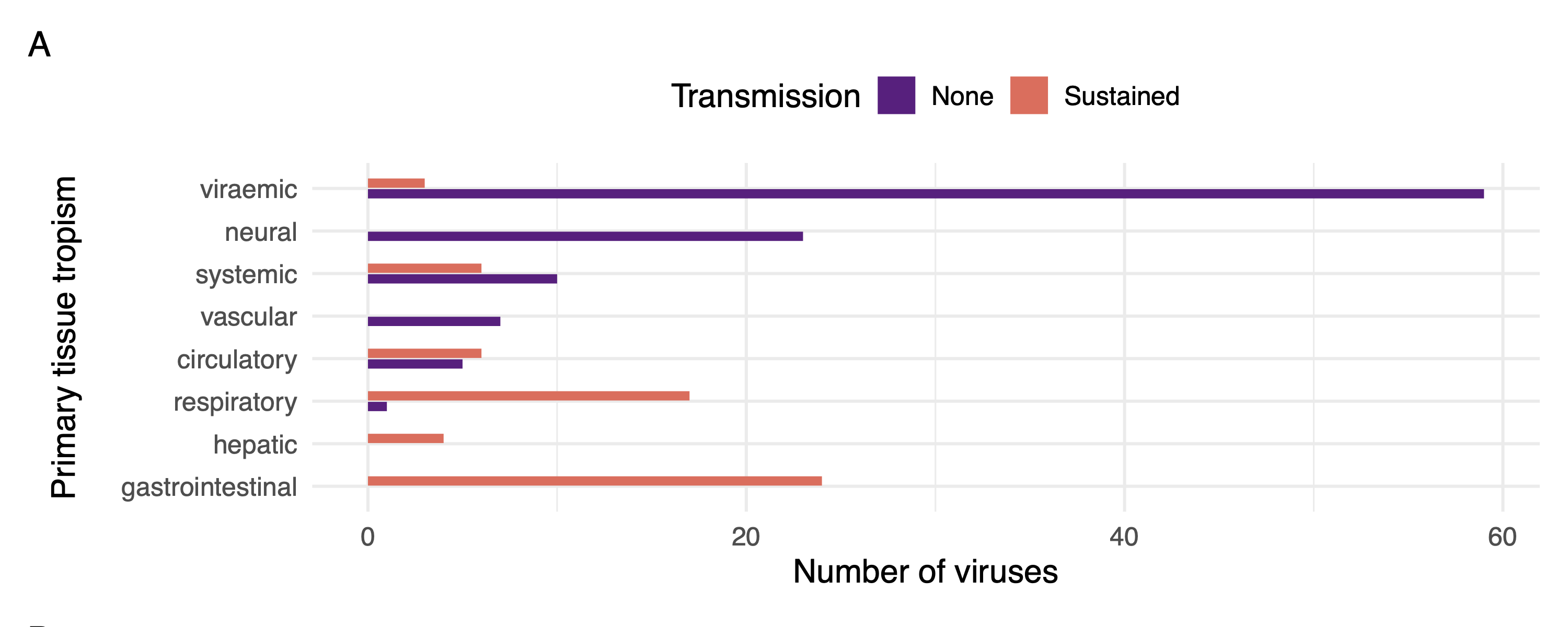
Brierley, Pedersen, and Woolhouse (2019)
RNA virus virulence
Leaves: correct classifications.

Brierley, Pedersen, and Woolhouse (2019)
Zoonotic virus case fatality rates

Guth et al. (2019)
Immune system divergence
Humans have very acidic stomachs
Humans are very sensitive to LPS (Brinkworth and Valizadegan 2021)
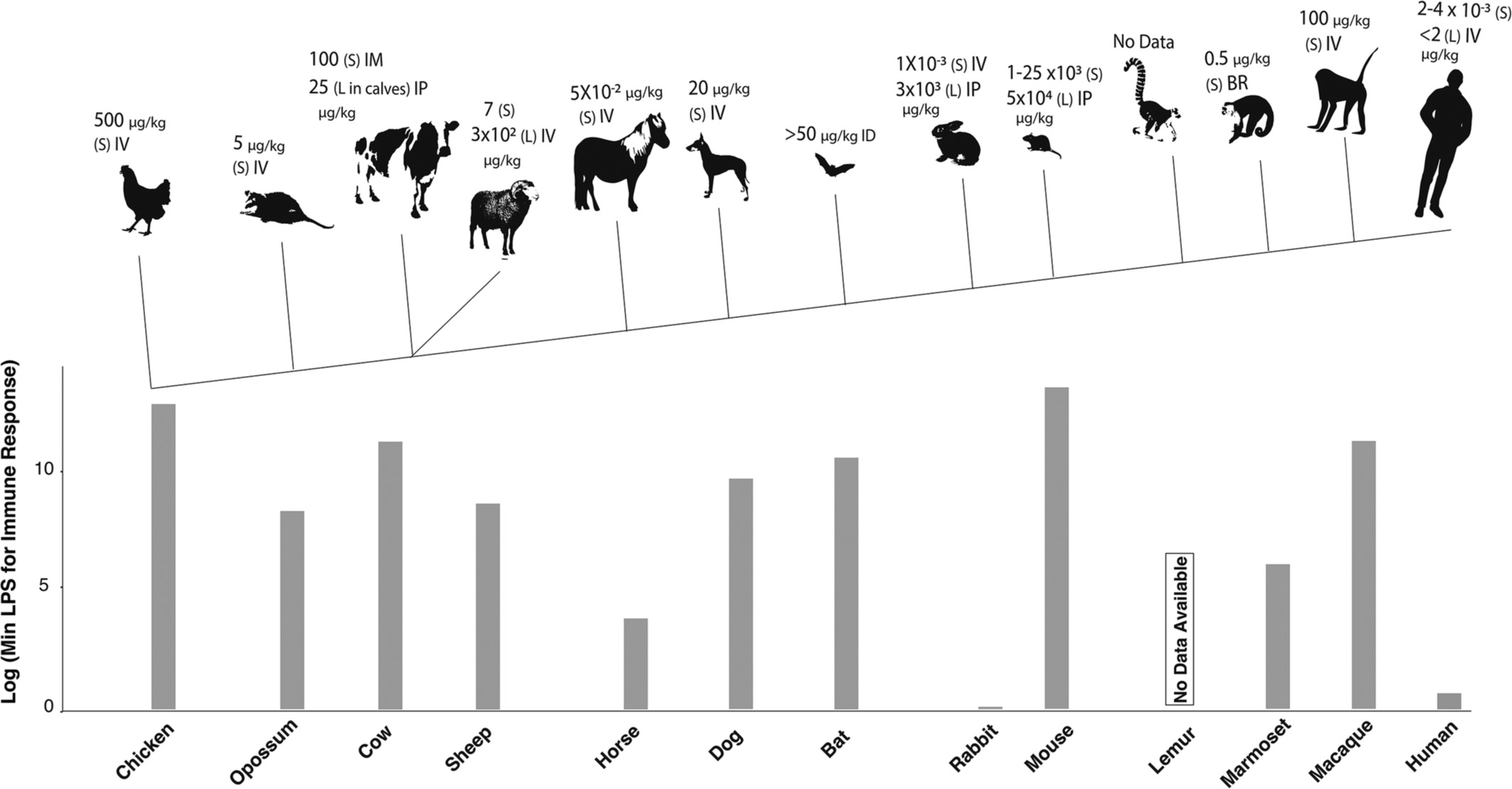
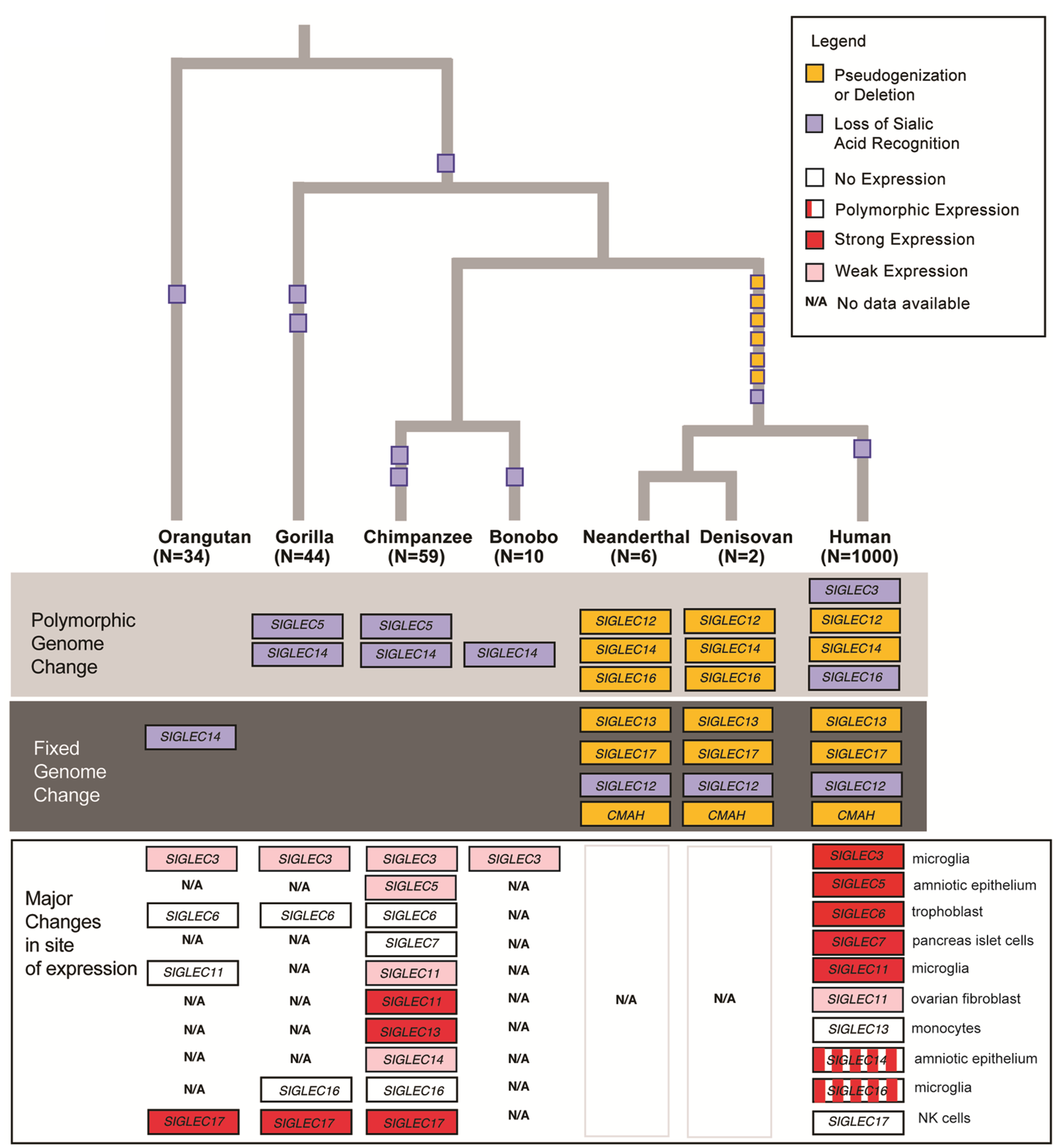
CMAH loss of function (Khan et al. 2020)
Human-specific downregulation of anthrax receptor protein (ANTXR2) (Choate et al. 2021)
Inflammation of animal vs. plant foods (Shivappa et al. 2014)
Substance use
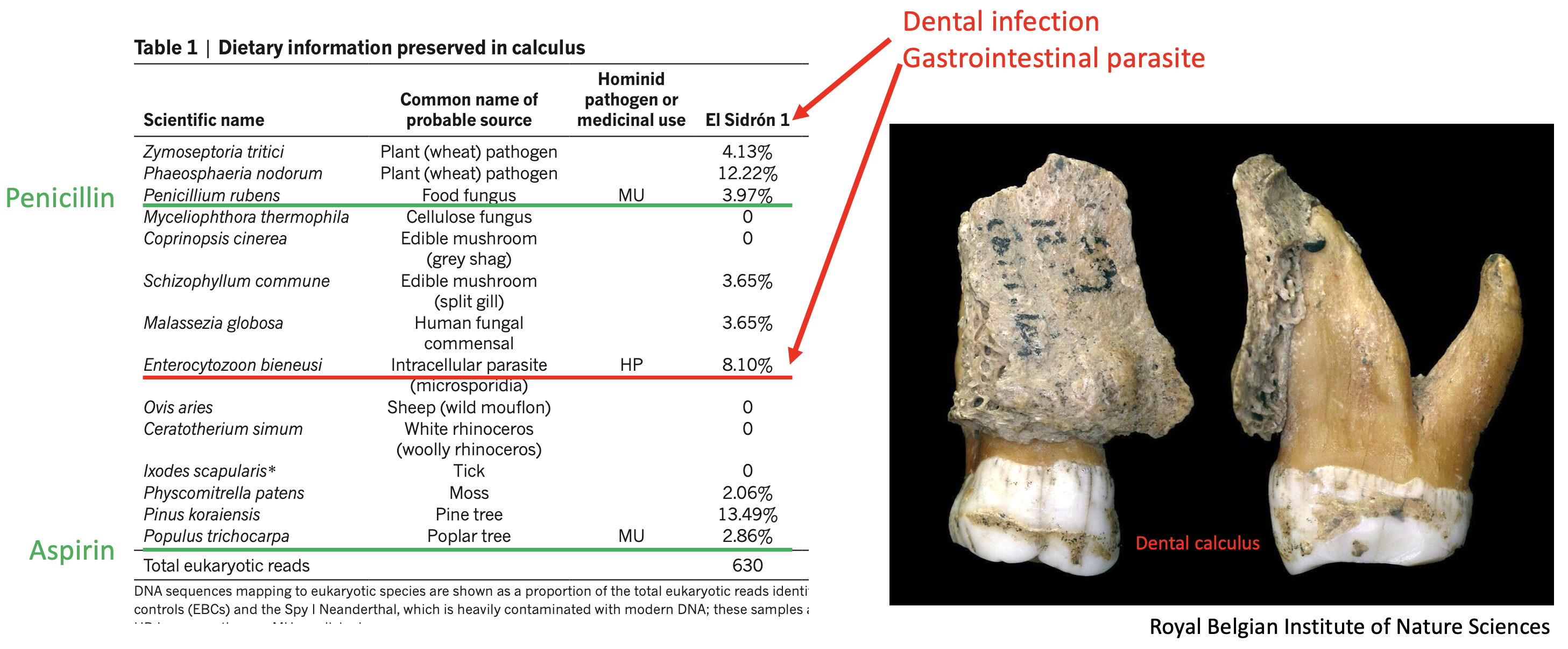
Neanderthal medication? (Weyrich et al. 2017)
Spices and health outcomes (Rakhi et al. 2018)
Most popular recreational plant drugs are toxic to macroparasites (nicotine, caffeine, THC, betel nut, cocaine)
Tobacco shamans
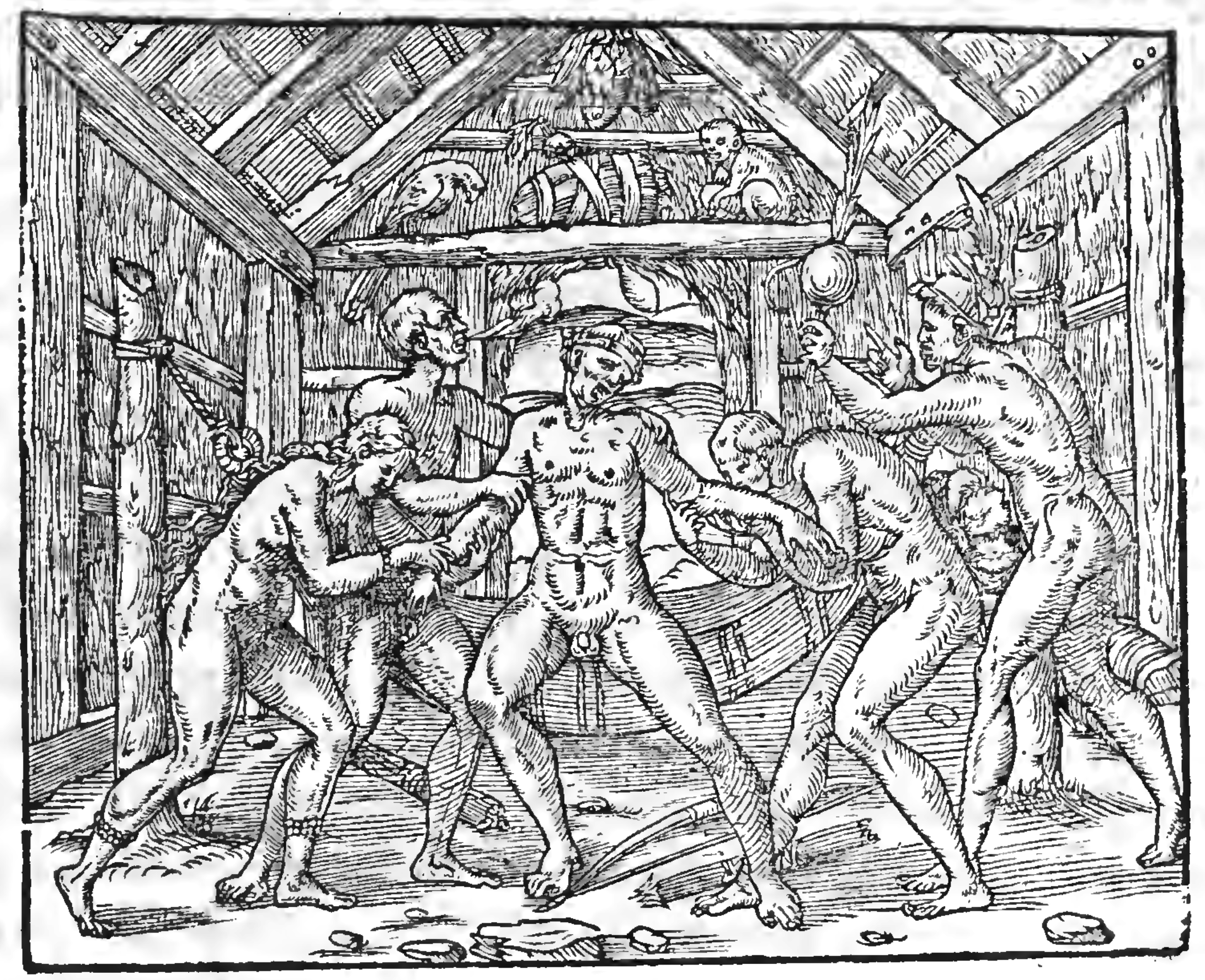

Brazilian Tupinamba curing by blowing tobacco smoke. Andre Thevet, La Cosmographie Universelle, 1575
Helminths vs. tobacco use in Aka foragers
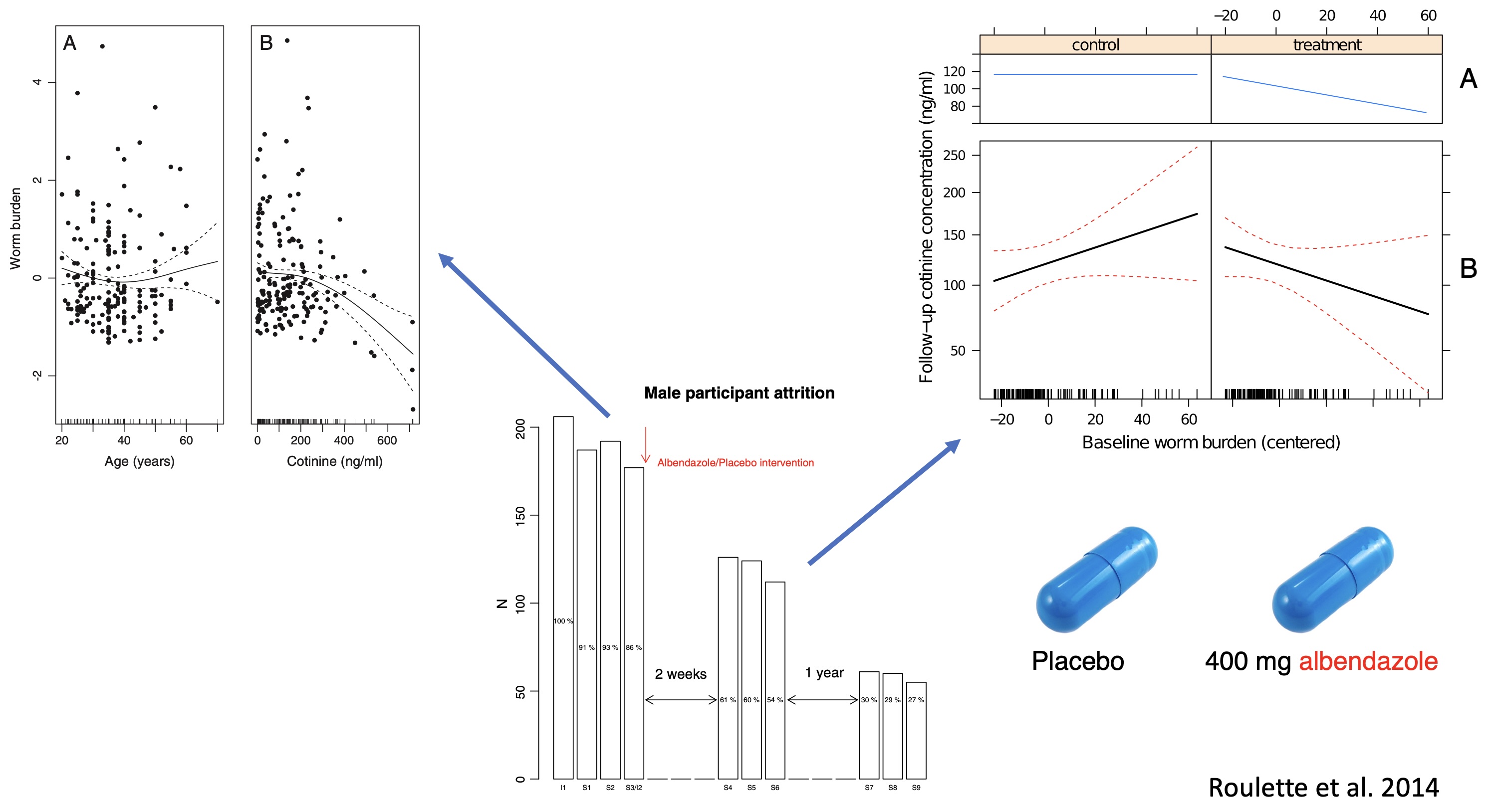
Tobacco use by age and sex
Theoretical model
Age of first use
Caffeine in a representative US sample (N = 2714)
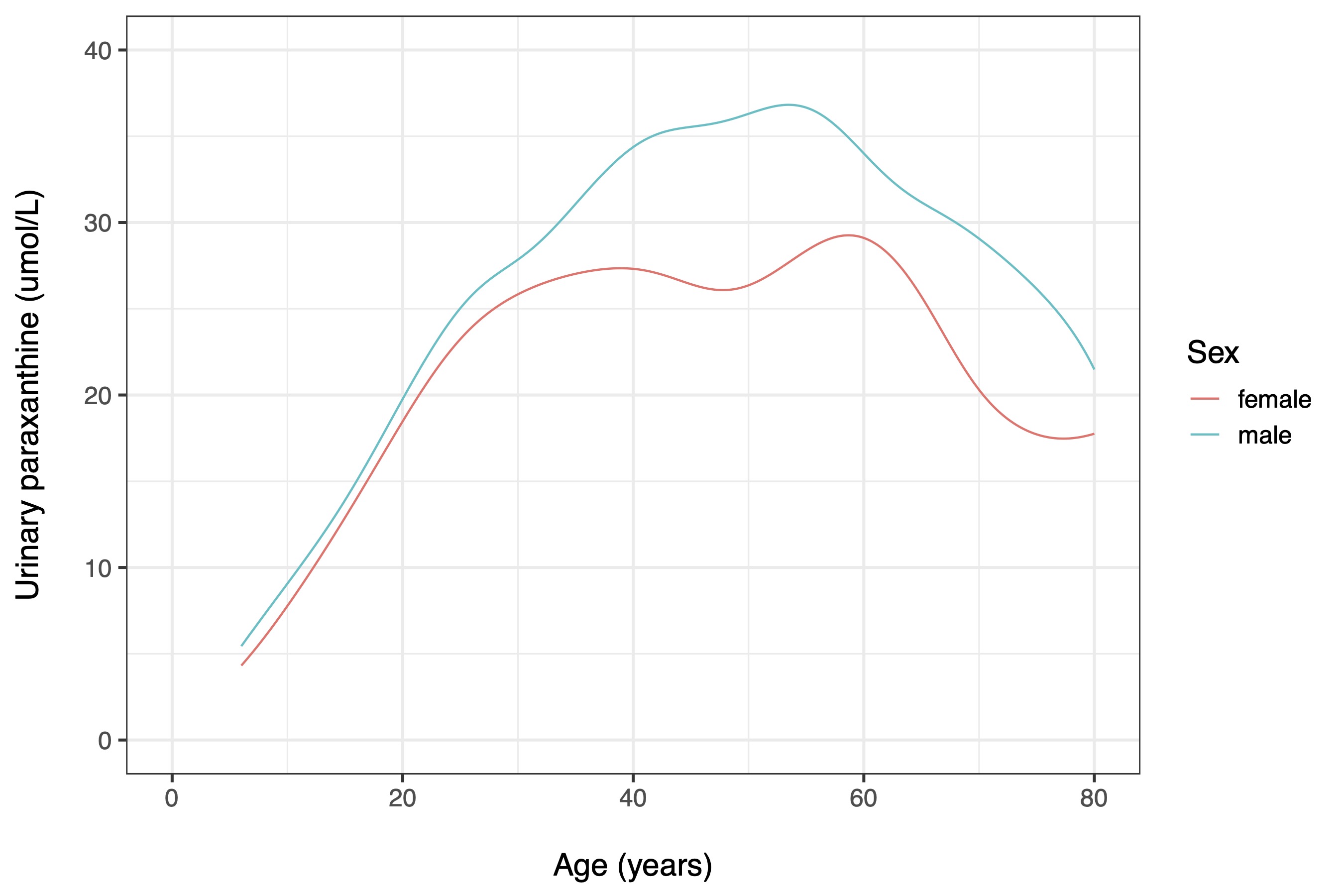
Female tobacco use by age in 66 low- and middle-income countries (N = 2.6M)
Male tobacco use by age in 66 low- and middle-income countries (N = 1.1M)
Tobacco use by age in 66 low- and middle-income countries (N = 3.7M)
Tobacco use by years of education in 66 low- and middle-income countries (N = 3.7M)
Tobacco use by reproductive variables in 66 low- and middle-income countries (N = 3.7M)
- Marriage: Women aOR = 0.76 (0.7, 0.84); Men aOR = 1.2 (1.1, 1.3)
- Pregnancy: aOR = 0.85 (0.77, 0.94)
- Breastfeeding: aOR = 0.89 (0.81, 0.98)
Concluding remarks
- The human niche involved fewer anti-infective plant foods and more infective animal foods
- Theories often emphasize meat spoilage but ignore spillover risk
- Zoonotic pathogens often have poor transmissibility but high virulence
- A single lifetime infection of a rabies-like pathogen would have had an enormous impact on fitness
- The human immune system appears to have diverged from those of ape relatives
- There is evidence of tobacco and other pharmacological plants in the Pleistocene
- Spices and common recreational plant drugs appear to provide medical benefits
- Drug toxicity shapes global patterns of use by age, sex, and reproductive status
Rabies as a model zoonotic disease
- Seven lyssaviruses infect humans
- Transmission: bites from infected bats and carnivores
- Infects the nervous system
- 100% lethal (without immediate treatment)
- 13K–59K annual deaths globally (mainly from rabid dogs)
- No human-to-human transmission